Understanding Ear Infections
Causes of Ear Infections:
Ear infections typically occur when bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, which is the space behind the eardrum. The most common cause is a respiratory infection, such as a cold or flu, which can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. Other factors that can contribute to ear infections include allergies and sinus infections
Symptoms of Ear Infections:
The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the age of the individual and the severity of the infection. Common signs and symptoms include:
1. Ear pain or discomfort
2. Fluid drainage from the ear
3. Difficulty hearing or temporary hearing loss
4. Irritability, especially in infants and young children
5. Fever
6. Headache
7. Loss of appetite
Types of Ear Infection:
1. Otitis Externa (Outer Ear Infection): This type of infection affects the outer ear canal, which is the portion of the ear that extends from the outside of the ear to the eardrum and is often caused by bacteria or fungi. Symptoms may include ear pain, itching, redness, swelling, and discharge.
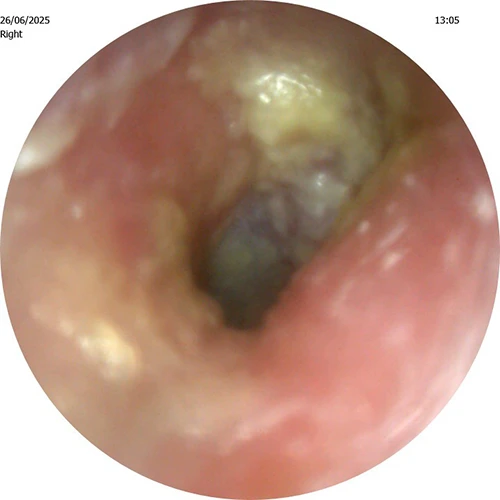
2. Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Otitis media occurs in the middle ear, which is the space behind the eardrum. It is usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection, often resulting from a cold or respiratory infection. Symptoms may include ear pain, fluid drainage from the ear, hearing loss, fever, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
3. Otitis Interna (Inner Ear Infection): Otitis interna, also known as labyrinthitis, affects the inner ear. It is typically caused by a viral or bacterial infection that spreads from the middle ear. In addition to ear pain, symptoms may include dizziness, vertigo, hearing loss, nausea, and vomiting.
4. Chronic Otitis Media with Effusion: This type of ear infection involves long-lasting fluid buildup in the middle ear without an active infection. It often occurs after an acute middle ear infection has resolved. Symptoms may include hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and occasional mild pain or discomfort.
Treatment Options:
The appropriate treatment for an ear infection depends on several factors, including the age of the individual, the severity of the infection, and the presence of any underlying conditions. In many cases, ear infections resolve on their own without medical intervention if they do not you must seek the advice of a health care professional immediately. Certain treatment options may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and promote healing:
1. Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relief, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen, can help reduce ear pain and discomfort.
2. Warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can provide temporary relief from pain.
3. Antibiotics: If the ear infection is bacterial or if it persists or worsens, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics to clear the infection.
4. Ear tubes: In some cases, particularly for recurrent or chronic ear infections, a surgical procedure may be recommended to insert small tubes into the eardrums. These tubes help equalize pressure and promote fluid drainage, reducing the likelihood of future infections.
Prevention:
While it may not be possible to prevent all ear infections, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk:
Practice good hygiene: Regularly washing hands and keeping the ears clean can help prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses.
Stay up to date with vaccinations: Vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and the flu vaccination, can help prevent certain infections that can lead to ear infections.
Earwax removal. A heavy build up of earwax is an ideal breeding ground for infection. At Waxaxe we are able professional remove earwax safely using specialised equipment. To book an appointment call Ben on 07598 303 877.
Conclusion:
Ear infections can be a source of discomfort and pain. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals and parents make informed decisions about managing and preventing ear infections. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
